This article is the first in a series in which I will annotate concepts related to the architecture, technologies, and organization of a service implemented using the .NET 8 framework.
An example project that demonstrates the concepts we will discuss is available in this repository https://github.com/maurizioattanasi/ATech.MovieService
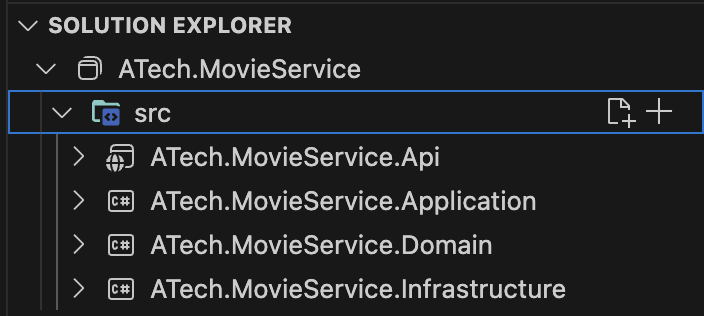
I will begin by describing the anatomy of the solution of a typical service.
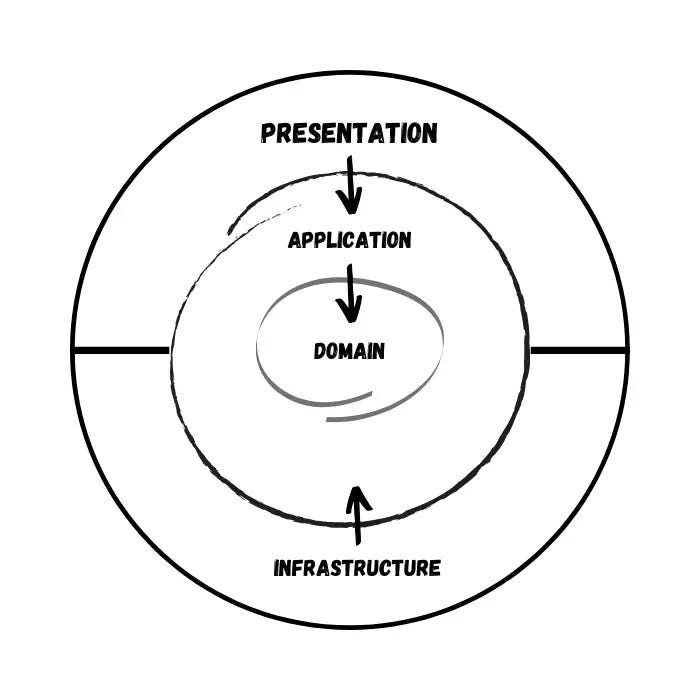
The image above is one of the possible representations of onion architecture, one of the concepts defined by clean architecture, a software design pattern that offers several advantages, particularly in terms of maintainability, testability, and flexibility.
Each of the layers represented in the image corresponds to a project of the solution.
| Project Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| ATech.MovieService.Domain | The Domain layer encapsulates the heart of the domain models and business logic. | classlib |
| ATech.MovieService.Application | The Application layer manages business logic, harnessing the services of the Domain and Infrastructure layers. | classlib |
| ATech.MovieService.Infrastructure | Infrastructure manages database access and external services. | classlib |
| ATech.MovieService.Api | Presentation layer that enables interaction with users or external systems, using the services provided by the Application layer. | web |
The three layers are injected as services in Program.cs.
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
...
{
builder
.Services
.AddPresentation()
.AddApplication(configuration)
.AddInfrastructure(configuration);
}
- Presentation Layer: The AddPresentation() method registers services related to the presentation layer, which typically includes controllers, views, and other UI components.
- Application Layer: The AddApplication(configuration) method registers services for the application layer, which contains the business logic and application-specific rules.
- Infrastructure Layer: The AddInfrastructure(configuration) method registers services for the infrastructure layer, which handles data access, external services, and other infrastructure-related concerns.
By organizing the code in this manner, the application adheres to the principles of Onion Architecture, promoting a clear separation of concerns and dependency inversion. This ensures that each layer interacts with the others through well-defined interfaces, enhancing maintainability and testability.
Enjoy, ![]()